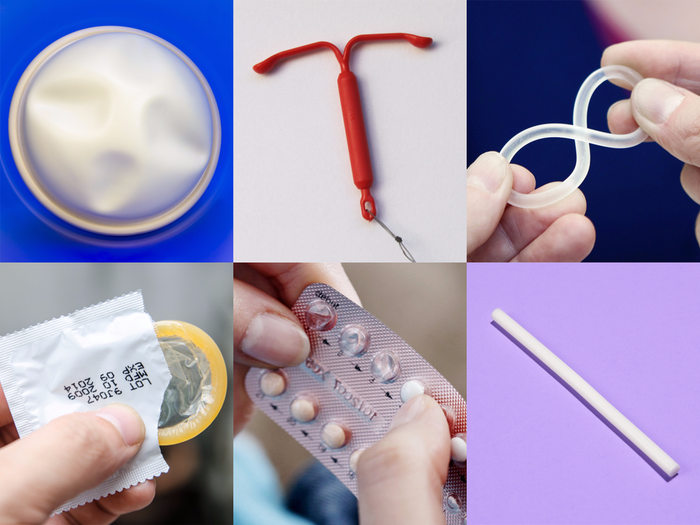
You can avoid getting pregnant by using birth control, which is sometimes referred to as contraception. Birth control comes in a variety of forms. Only when it is applied appropriately can birth control be effective. Spend some time learning about each method of birth control and how to use it.
Use birth control if you wish to avoid having children and are sexually active. Anytime you engage in unprotected sex, you run the risk of becoming pregnant.
Which birth control works the best?
You can choose the method that is most effective for you and your partner by learning more about birth control options. When deciding, take these things into account:
- Comfort level or simplicity of the procedure.
- Ability to successfully avoid pregnancy (with correct use).
- Protection from sexually transmitted diseases (STIs).
- Your age and general well-being.
- Pregnancy preparations.
- Symptoms or dangers.
- How many partners you have or how frequently you have sex.
- Privacy (how crucial it is to keep your birth control method a secret) (how important it is to keep your birth control method a secret).
- Added advantages include less painful periods and predictable menstrual cycles.
How does birth control work?
Each method of birth control functions a little bit differently. It operates in a variety of ways, such as:
- Stopping sperm from getting to an egg.
- Preventing the release of an egg from your ovary.
- Sperm is damaged such that it cannot swim to an egg.
- Causing your cervical mucus to thicken so that sperm cannot pass through it.
- Altering the uterine lining’s thickness to prevent egg implantation
What birth control methods are most effective?
The best method of birth control is to abstain from sexual activity (abstinence). This can be challenging to sustain, even for couples who are highly motivated. It’s crucial to plan ahead and have a backup method of birth control in mind.
Birth control only functions when it is applied correctly and regularly. The most effective birth control methods are typically those that are easier to use and don’t need much upkeep. These methods include sterilization, intrauterine devices (IUDs), and birth control implants.
The least effective forms of birth control, such as pulling out or fertility awareness, are those.
It’s usually ideal to use two forms of birth control, such as a condom and a birth control pill. This is because you are simultaneously employing a barrier method, taking hormone medication, and protecting yourself from STIs.
What birth control methods are there?
Discuss birth control with your spouse and your healthcare practitioner before deciding on a technique. Birth control methods only work when they are used correctly. Make sure you are familiar with how to apply the technique you select.
Among the birth control options are:
- Barrier techniques: Sperm cannot enter your uterus using barrier techniques. Every time you have sex, a barrier mechanism is used.
- Drugs and gadgets that employ hormones to suppress ovulation or alter the environment in your uterus and cervix are known as hormonal techniques. Some hormone treatments are daily (short-acting), while others are inserted by your doctor into your arm or uterus (long-acting).
- Sterilization: Sterilization is the surgical process of permanently ending pregnancy. There are sterilization techniques for both men and women.
- Fertility knowledge Natural birth control strategies are used in the field of fertility awareness. Another name for this is natural family planning.
- If your birth control stops working, emergency contraception protects you from becoming pregnant. This can be viewed as your final “safety net” against pregnancy.
BARRIER METHODS
Condoms
A condom is a thin covering that is rolled over an erect penis and is composed of lambskin, latex, or plastic. Semen, the fluid containing sperm, is kept out of your vagina by the covering. Because they are prone to tearing or ripping, condoms are less effective than other birth control options.
What does it do?
Before sexual activity, a condom is placed over an erected penis. Every time you have sex, use a fresh condom.
How do I obtain it?
Condoms are typically available at drug or supermarket stores.
How well does it work?
If used prior to sexual activity and do not rip, condoms are approximately 85% effective.
What else do I need to know?
Condoms are among the finest methods of STI prevention, despite the fact that they don’t offer 100% protection. Condoms should only be used with water-based lubricants, such as K-Y Jelly® or Astroglide®. Condoms can be damaged by lubricants made of oil, such as Vaseline® or baby oil. You should think about using emergency contraception if a condom breaks.
Spermicide
It is what?
A gel, cream, or suppository called spermicide stops sperm from getting to an egg. Because of the compounds in it, sperm cannot swim up to an egg. Spermicide must be used precisely as instructed in order to be effective. Another spermicide-like vaginal gel is available on prescription only. It functions by reducing the pH in your vagina, which hinders sperm’s ability to swim.
What does it do?
You apply vaginal gels and spermicide to your vagina at least 15 to 30 minutes before engaging in sexual activity. The majority of spermicides last for around an hour before needing to be reapplied. Every time you have sex, reapply spermicide and don’t wash it off.
How can I obtain it?
The majority of drug or supermarket stores sell spermicides. A prescription is required to purchase the pH-lowering vaginal gel (Phexxi®).
How effective is it?
Spermicide is only 70% efficient at preventing pregnancy when used on its own. Spermicide can be 94% effective when used with another barrier technique of pregnancy control. A vaginal gel (prescription only) is 85% to 93% effective.
What else should I understand?
Spermicide does not provide any STI prevention. In fact, it might put you at more danger. This is because spermicide contains chemicals that irritate your vagina and make it simpler for an infection to enter your body.
Diaphragm
What is it?
A flexible, reusable dome-shaped cup called a vaginal diaphragm is placed into the vagina to prevent conception. By restricting your cervix, it prevents sperm from entering your uterus. Use a diaphragm and a water-based spermicide or contraceptive gel.
How is it used?
A diaphragm has the appearance of a tiny cap or cup. To cover your cervix, you fold it in half and slip it up into your vagina. One to two hours prior to sex, place your diaphragm. Six to twenty-four hours after having intercourse, remove it. For optimal protection, apply spermicide to the diaphragm’s rim before sexual contact.
How do I get it?
Different diaphragm sizes are available. To be fitted for a diaphragm, it necessitates seeing a doctor for a pelvic check. It’s crucial to get a diaphragm that fits properly. Your diaphragm might need to be adjusted if you lose or gain more than 10 to 15 pounds. However, some diaphragms, such as the Caya®, are universal and don’t need to be fitted.
How well does it work?
Vaginal diaphragms have an average effectiveness of 87%, although they can have a maximum effectiveness of 94% when used correctly (with spermicide) and regularly.
What else do I need to know?
A diaphragm and spermicide do not provide protection from all STIs, including HIV (the virus that causes AIDS).
Coccyx cap
It is what?
A cervical cap fits tightly over your cervix and is shaped like a thimble. It is composed of silicone or soft rubber.
What does it do?
First, apply spermicide to the cap. Next, place the cap against your cervix in your vagina. The spermicide paralyzes the sperm, and the cap closes your cervix. The cervical cap can be inserted up to six hours before sex. After having sex, wait at least eight hours before removing your cervical cap. You can leave the cap on for up to 48 hours. Use spermicide precisely as instructed.
How do I obtain it?
To be fitted for a cervical cap, you must see your doctor and have a pelvic examination. Similar to a diaphragm, it works best when it fits properly.
How well does it work?
When used in conjunction with a spermicide, a cervical cap can increase its effectiveness to 85%, which is roughly 78%.
What else do I need to know?
As opposed to condoms, using a cervical cap and spermicide provides less protection against STIs.
Female Condom
What is it?
A female condom is a plastic tube that has been greased with flexible rings on both ends. The tube has a closed termination at one end.
How is it used?
Place the condom in your vagina such that the closed end covers your cervix and the other end just touches your labia before engaging in sexual activity (the lips on the outside of your vagina). In your uterus, the condom prevents sperm from entering. After having sex, you immediately take the condom off.
How can I get it?
Pharmacy and grocery stores sell female condoms that you can purchase without a prescription.
How well does it work?
About 21% of women use a female condom annually, but they still get pregnant.
What more should I know?
The best defense against STIs is a male condom, but female condoms can provide some level of security.
Sponge
It is what?
A tiny, donut-shaped device called a vaginal sponge holds spermicide. Sperm and your cervix are separated by it.
How does it function?
You insert the sponge into your vagina and cover your cervix with it after wetting it with water. It starts to release spermicide once it’s wet. A 24-hour supply of spermicide is present in the sponge. This indicates that you can take it up to 24 hours before having intercourse. After intercourse, always keep it in place for six hours. A sponge shouldn’t be left in your vagina for longer than 30 hours.
How can I get it?
The sponge is widely available in drug and supermarket stores without a prescription.
How well does it work?
The effectiveness of a birth control sponge in preventing conception ranges from 76% to 91% (depending on if you use it correctly). Additionally, the sponge works better if you have never given birth.
What else do I need to know?
The sponge does not offer STI protection and is linked to higher rates of vaginal infections.
HORMONAL DEVICES

Birth Control Implant
What is it?
Your healthcare professional will insert a tiny rod called a Nexplanon® (the size of a matchstick) under the skin of your upper arm. It lasts roughly three years before needing to be removed or replaced and releases a consistent stream of the progestin hormone. Because it takes little to no care, doesn’t obstruct spontaneous sex, and can be concealed, some people prefer the ease of an implant.
How are birth control implants placed by doctors?
In their office, a medical professional installs the implant. To begin with, they numb the inside of your upper arm so that you won’t feel any pain. The implant is then implanted just below the surface of your skin using an applicator. They apply a bandage on the area. You cannot remove your birth control implant yourself; a healthcare professional must do so.
How do I get it?
An implant for birth control must be prescribed by a medical professional.
How well does it work?
Implants for birth control are nearly 100% effective. It is the most potent type of reversible contraception that is currently available.
What more should I know?
Contraceptive implants come with risks and might not be right for you. The most frequent side effect of an implant is irregular bleeding, even though the bleeding is typically not very severe. This typically improves after six to twelve months, but for some people, their periods completely stop. Additional side effects include breast pain and headaches.
Intrauterine device (IUD)
What is it?
A small, flexible, T-shaped device called an intrauterine device (IUD) is inserted into the uterus to prevent conception. IUDs come in two categories:
- An IUD made of copper.
- IUD composed of plastic that contains hormones (progestin).
For ten years, the copper ParaGard T380A® can remain in situ. The copper blocks the passage of sperm via your uterus and vagina to reach an egg.
The progestin IUDs include:
- Mirena® (lasts seven years)
- Liletta® (lasts six years)
- Kyleena® (lasts five years)
- Skyla® (lasts three years)
These IUDs function by making your cervical mucus thicker, which prevents sperm from reaching an egg. Additionally, the hormone thins the lining of your uterus, which results in lighter monthly flow.
How is it used?
One of the “get it and forget it” methods of birth control is the IUD. This implies that once you have it, you may forget about it because it requires neither daily nor monthly upkeep.
How can I get it?
A medical professional inserts the IUD into your uterus after doing a pelvic checkup. Only those with a prescription can get it.
How well does it work?
The IUD has a nearly 100% success rate.
Does an IUD hurt?
IUDs shouldn’t hurt, so no. After your healthcare professional inserts it, you may experience discomfort or minor cramping. The same is true while removing your IUD; there can be some minor discomfort.
What else do I need to know?
The type of IUD you have will determine the side effects. Period pain and heavy bleeding may increase with copper IUD use. IUDs made of copper are preferred by some since they don’t contain hormones. Uneven bleeding is the progestin IUD side effect that occurs the most frequently. Usually, this gets better after six to twelve months. Some people may also entirely cease having periods. Your IUD must be removed by a professional. There is a higher likelihood that an ectopic pregnancy will arise in the extremely unlikely event that a pregnancy occurs while wearing an IUD.
Within 120 hours (five days) of having unprotected sex, IUDs can potentially be used as emergency contraception. Actually, it performs better than the morning after pill as an emergency contraceptive.
Hormonal contraception
contains estrogen-containing birth control pills, the NuvaRing® vaginal ring and the Xulane® patch.
What is it?
You can prevent pregnancy by taking the pill, the patch, or the ring. The vaginal ring is placed once a month, the pill is taken daily, and the patch is changed every week. The majority of hormonal contraceptives use two hormones (estrogen and progestin). These methods of birth control all function by suppressing ovulation.
What does it do?
Every day at the same time, you take a medication. There are numerous distinct categories of pills. Others permit longer intervals between periods or none at all. Some are made to allow for a monthly period. A vaginal ring is changed every month to accommodate your menstruation. Through your skin, a birth control patch distributes hormones. Every week, you should change your patch. All of these techniques call for steady, routine use. It can lead to irregular menstrual periods and the possibility of pregnancy if you neglect to use it.
How do I obtain it?
Only with a prescription is hormonal birth control available.
How well does it work?
If used properly, combined hormonal contraceptives have a chance to be 99% effective. The effectiveness is only about 91%, though, because most people don’t use it properly. Hormonal contraception, such as the pill, is significantly more successful than barrier measures like condoms, but not being as effective as an IUD or implant.
What else do I need to know?
In the initial few months of use, the medication may have a few mild adverse effects, including:
- Breast tenderness/pain.
- Nausea.
- Headaches.
- Irregular periods.
Your risk of blood clots increases when using estrogen-containing contraception. To determine whether estrogen-containing contraception is the best option for you, consult a healthcare professional. Hormonal contraception has advantages including lighter, more regular periods and less cramping during the menstrual cycle. Acne and PMS symptoms may also become better for birth control pill users.
Progestin only pills (mini pills)
What is it?
These birth control tablets only have one hormone in them (progestin).
How do they work?
Minipills function by making your cervical mucus thicker, preventing sperm from reaching an egg. The hormone in the pills thins the lining of your uterus as well, resulting in lighter monthly bleeding. It’s crucial that you take a minipill at the same time every day for the minipill to be as effective as possible. Minipills that contain solely progestin can be purchased with a prescription.
How effective is it?
Progestin-only birth control tablets can be 99% effective, much like combination birth control pills. They are actually only 91% effective because the majority of users don’t use them properly.
What else should I know?
A progestin-only pill’s most frequent adverse effect is irregular bleeding, however the bleeding is typically mild. Usually, this gets better after six to twelve months. For those who cannot take estrogen or are nursing (chestfeeding), the minipill is an acceptable substitute.
Depo-provera® (birth control shot or Depo)
What is it?
An example of the hormone progestin is Depo-Provera®. In order to prohibit sperm from reaching an egg, it stops you from ovulating and thickens the cervical mucus.
What does it do?
It is an injectable to administer birth control. It is injected into your upper thigh or arm by your doctor. Each shot protects against pregnancy for almost 12 weeks (or three months). Some providers let you administer a low-dose version (Depo-Subq Provera 104®) to yourself at home.
How can I get it?
A doctor must write a prescription for Depo-Provera®. You’ll receive the hormone injection in their office. If you use the injection with a lower dose, you might be able to inject yourself at home.
How well does it work?
The Depo-Provera® shot has a potential effectiveness of 99%. However, because they don’t receive their injections on schedule, 6% of persons who receive the shot each year become pregnant.
What else do I need to know?
Taking Depo-Provera may result in erratic bleeding. When using the medicine for more than a year, women cease getting their period. Only this contraception has the potential to increase body weight. Once you stop taking Depo-Provera, it could be a little more difficult to estimate when your fertility will return (compared to other birth control methods).