Pleural mesothelioma is a cancer of the lining of the lungs, known as the pleura. It is brought on by breathing in asbestos fibers. 80–90% of mesothelioma diagnoses are malignant pleural mesotheliomas. Shortness of breath, a dry cough, and chest pain are all signs of pleural mesothelioma.
What Is Pleural Mesothelioma?
Malignant pleural mesothelioma is a very uncommon cancer of the lining that surrounds the lungs, called the pleura. Fibers from asbestos are to blame. The fibers may embed in the pleura after inhalation, leading to swelling and scarring. These processes have the potential to grow into mesothelioma tumors over time.
Pleural Mesothelioma Facts
- The most prevalent type of mesothelioma cancer is pleural malignant mesothelioma.
- Pleural mesothelioma signs and symptoms include shortness of breath, tiredness, and chest pain.
- Despite some pleural mesothelioma patients’ long-term survival following rigorous therapy, the disease is not thought to be curable.
- The prognosis for a patient varies according to their unique circumstances, with an average life expectancy of roughly 18 months.
- Pleural mesothelioma is detected in roughly 2,500 persons yearly.
- Numerous tests, such as scans and biopsies, are frequently used to make a diagnosis.
- Chemotherapy, surgery, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy are frequently used to treat pleural mesothelioma.
What Is the Prognosis for Pleural Mesothelioma?
The prognosis for pleural malignant mesothelioma relies on a variety of variables, much like for other kinds of malignant mesothelioma. The median survival time for people who do not receive treatment is six months. However, some medical procedures, such as surgery and chemotherapy, can lengthen life expectancy.
| Pleural Mesothelioma Survival Rates | |
|---|---|
| 1 year after diagnosis | 73% |
| 3 years after diagnosis | 23% |
| 5 years after diagnosis | 12% |
| 10 years after diagnosis | 4.7% |
The following are the most significant mesothelioma prognostic factors for patients with pleural malignant mesothelioma:
- Cell type (histopathology)
- Stage of mesothelioma
- Patient’s gender and age
Epithelioid cell type, which is the most prevalent, is the diagnosis for the majority of pleural mesothelioma patients. Epithelioid cells often form in solid sheets or cord configurations, which means they stick firmly to one another and slow the rate of metastasis. They also respond to treatment the best. Patients with epithelioid cell-type pleural mesothelioma typically live for 19 months after diagnosis.
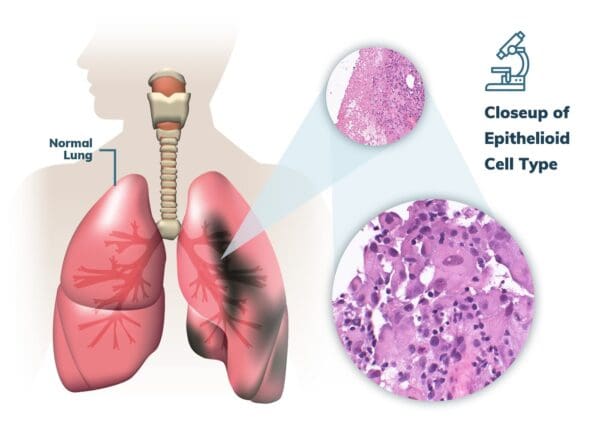
Sarcomatoid and biphasic cells are less frequent but have worse prognoses than epithelioid cells. Patients with sarcomatoid mesothelioma have a prognosis of roughly eight months since the cancer seldom responds to therapy and frequently metastasizes.
Depending on whether epithelioid or sarcomatoid cells predominate, patients with biphasic pleural mesothelioma have an intermediate life expectancy.
According to recent research, people with malignant pleural mesothelioma have been living longer generally over the past ten years as accessible treatments and diagnostic techniques have improved. Long-term survivors are now emerging among some patients. In 2005, Heather Von St. James received a pleural mesothelioma diagnosis with a 15-month initial prognosis. She received therapy, and she has been cancer-free for more than 15 years.
What Causes Pleural Mesothelioma?
Inhaling asbestos fibers can result in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Mineral slivers can enter the pleura via passing through lung tissue. Inflammation is brought on over time by asbestos fibers. The fibers have the potential to activate biological processes that destroy DNA. Tumors from mesothelioma may therefore form.
Other factors may contribute to the development of mesothelioma, including:
- Erionite exposure: Erionite is a natural mineral similar to asbestos. It has been linked to mesothelioma and lung cancer.
- Radiation exposure: Radiation treatments for cancer can damage healthy cells, potentially leading to cancer. Prior radiation therapy has been tentatively linked to mesothelioma.
What Are the Symptoms of Pleural Mesothelioma?
Pleural mesothelioma symptoms might appear 10 to 50 years after asbestos exposure. Usually, the respiratory system and chest is where symptoms starts.
Pleural Mesothelioma Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Difficulty swallowing
- Dry cough
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Fluid in the lung (pleural effusion)
- Night sweats
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Weight loss
There may be new and worsening symptoms as the condition progresses. For instance, coughing up blood and trouble swallowing may be stage 4 pleural mesothelioma symptoms.
Patients with pleural malignant mesothelioma may also be diagnosed with an asbestos-related disease, which can affect the start of symptoms.
Pleural Effusion
When an excessive amount of fluid gathers between the two layers of the pleura, pleural effusion results. The lungs may become compressed by this fluid, making it challenging to breathe. Breathing issues and pleural effusion are typical signs of pleural mesothelioma.
Pleural Plaques
Areas of thicker tissue on the pleura’s surface are known as pleural plaques. Pleural plaques frequently go unnoticed. One of the most frequent adverse outcomes of asbestos exposure is this disorder. Pleural plaques may indicate an increased risk of mesothelioma in asbestos-exposed people.
Pleural Thickening
Scar tissue causes the pleura to thicken, a condition known as pleural thickening. Malignant or benign pleural thickening are also possible. Exposure to asbestos and other inflammatory diseases are the main causes. One study found that pleural thickening occurs in most pleural mesothelioma patients.
Asbestosis
Inhaling asbestos fibers can result in asbestosis, a benign, long-lasting lung condition. This kind of pulmonary fibrosis exists. In the lungs of asbestosis patients, scar tissue forms. Breathing becomes harder as a result of the lungs becoming less flexible. Pleural mesothelioma may be more likely to develop in patients with asbestosis.
These asbestos-related conditions may also develop independently of pleural mesothelioma.
How Is Pleural Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
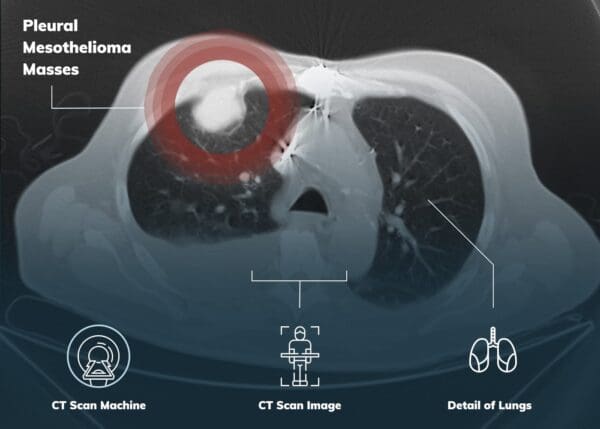
Multiple tests are frequently required for the diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma. To find tumors or metastases, one or more imaging scans, like an X-ray or CT scan, may be carried out first (spreading of disease). Blood tests may be carried out if a tumor is found to check for certain biomarkers (high levels of particular compounds in the blood), which can help distinguish mesothelioma from other illnesses.
A biopsy is now required in order to confirm a malignant pleural mesothelioma diagnosis. To collect a tissue or fluid sample for analysis, procedures such a thoracentesis or thoracoscopy may be used. A thoracentesis is a procedure where a doctor drains excess fluid from the chest by inserting a tiny needle.
Thoracoscopy is a more intrusive procedure. To examine the lungs and surrounding pleura, medical professionals introduce a viewing tube into the patient’s chest called a thoracoscope. Then they can take a sample of tissue or fluid for analysis. Following the biopsy, a pathologist will examine the cells to determine the exact type of cell and the course of the disease.
Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Stages
A mesothelioma expert will also establish the disease’s stage, or the extent of its spread, as part of the diagnostic procedure. The prognosis of a patient can be greatly influenced by their stage, which also influences the kind of treatments that are accessible.
| Pleural Mesothelioma Life Expectancy by Stage | |
|---|---|
| Stage 1 | 21 months |
| Stage 2 | 19 months |
| Stage 3 | 16 months |
| Stage 4 | 12 months |
The Tumor, Node, Metastasis (TNM) staging approach is the most popular method for determining the stage of pleural mesothelioma. The technique will be used by doctors to assign a score to a particular body part depending on the size of the tumor, if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, and whether it has reached distant organs.
While advanced stages of pleural mesothelioma may show distant metastases to lymph nodes and other organs, stage 1 and stage 2 pleural mesothelioma indicate minimal to no metastasis.
The medical team can create an efficient treatment strategy for a patient’s situation after the stage is identified.



31 Pings & Trackbacks
Pingback:blackhatlinks.com
Pingback:hookah store
Pingback:dumps shop
Pingback:Texas gun trader
Pingback:เครื่องฉีดน้ำแรงดันสูง ยี่ห้อไหนดี
Pingback:ร้านออกแบบสติ๊กเกอร์ ใกล้ฉัน
Pingback:buy magic mushrooms online
Pingback:mental health long island
Pingback:เดินบัญชี
Pingback:nagaqq
Pingback:코인선물
Pingback:magic mushrooms for sale online australia
Pingback:เตารีด ยี่ห้อไหนดี
Pingback:นำเข้าสินค้าจากจีน
Pingback:Dried Mushrooms
Pingback:Buy Nerve Pain Relief Online UK
Pingback:Mushroom Farm
Pingback:Dihydrocodeine 30mg
Pingback:yehyeh
Pingback:kupontoto
Pingback:Relx
Pingback:could mushrooms take over humans
Pingback:slotjili
Pingback:lsm99.review
Pingback:เว็บบอล Auto
Pingback:ขายคอนโด
Pingback:slots online
Pingback:พิมพ์สติ๊กเกอร์
Pingback:ร้านอาหารบ้านเพ
Pingback:psilocybin mushroom bars
Pingback:making silicone dolls